为什么要使用动态SQL?
开发人员在使用JDBC或者其他类似的框架进行数据库开发时,通常都要根据需求去手动拼装SQL,这是一个非常麻烦且痛苦的工作。而MyBatis的动态SQL功能刚好能解决这一问题。过 if, choose, when,
otherwise, trim, where, set, foreach等标签,可组合成非常灵活的SQL语句,从而在提高 SQL 语句的准确性的同时,也大大提高了开发人员的效率。
动态SQL标签大全:
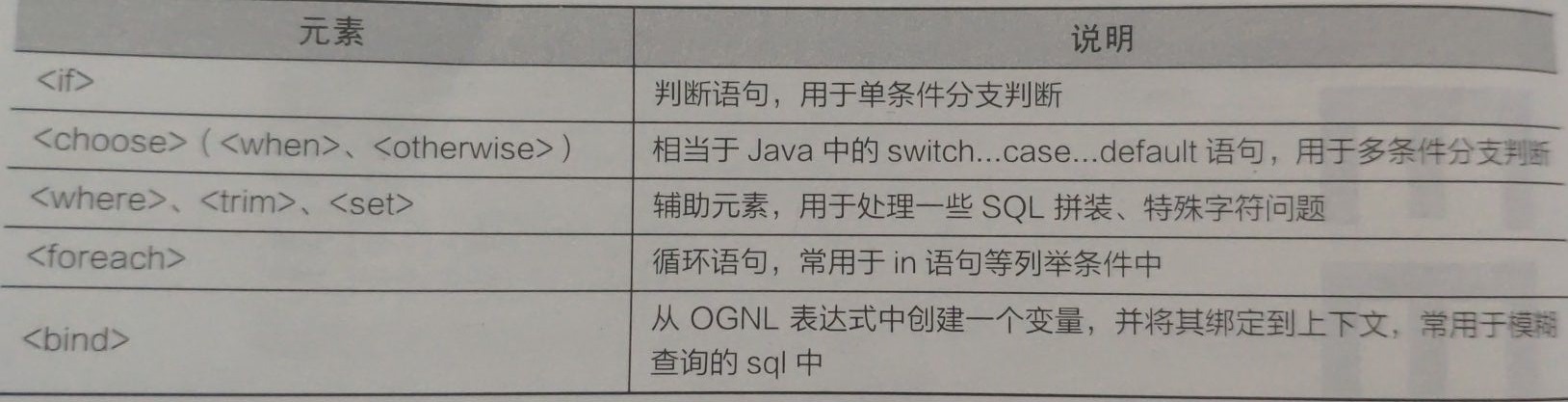
各个标签详解:
if标签
<select id="queryByIdAndTitle"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE 1=1
<if test="id!= null and title!=null">
AND id=#{id} and title=#{title}
</if>
</select>
注:if标签一般用于非空验证,如上例,若id为空,if标签里的代码,将不会执行,反之,则会执行。
问题:如果不用where 1=1直接用where将会出现SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE AND id=#{id} and title=#{title}的错误SQL语句。
choose(when、otherwise)标签
当遇到多个条件选择一个成立的条件时,if标签显然不合适,此时最合适的是类似于编程语言中分switch…case…而choose(when、otherwise)标签就类似于switch…case…的功能。
<select id="queryBy"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE 1=1
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</when>
<when test="name != null">
AND name like #{name}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND id= 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
注:choose(when,otherwise)标签相当于switch(case,default) ,如上例,若title 不为空,只执行第一个when标签里的代码,若title 为空,name不为空,只会执行第二个when标签里的代码,两个都为空,默认执行otherwise标签里面的代码。
where,trim,set标签
<select id="queryBy" resultType="com.scme.pojo.User" parameterType="com.scme.pojo.User">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="username!=null and password!=null">
and username=#{username} and password=#{password}
</if>
</where>
</select>
注:假设上例传入的username,password不为空,代码就可以运行成功!但朋友们可能有疑问了,实际上执行的sql语句是什么呢?其实,sql为:select * from user
where username=? and password=? 朋友们是否发现,where标签代替了sql中where关键字,但if中的and不见了。其实where标签可以自动去除是“AND”或“OR”开头的sql中的“AND”或“OR”关键字。
如果 where 元素没有按正常套路出牌,我们还是可以通过自定义 trim 元素来定制sql,实现where标签的效果。代码如下:
<select id="queryBy" resultType="com.scme.pojo.User" parameterType="com.scme.pojo.User">
select * from user
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
<if test="username!=null and password!=null">
and username=#{username} and password=#{password}
</if>
</trim>
<!-- 效果同上
<where>
<if test="username!=null and password!=null">
and username=#{username} and password=#{password}
</if>
</where> -->
</select>
set标签:
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.scme.pojo.User">
update user
<set>
<if test="username!=null">
username=#{username}
</if>
</set>
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id}
</if>
</where>
</update>
注:set标签功能和where标签差不多,set标签代替了sql中set关键字,set标签可以自动去除sql末尾的多余的“,”
< update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.scme.pojo.User">
update user
< trim prefix="set" prefixOverrides=",">
< if test="username!=null"> username=#{username} < /if>
< /trim>
< where>
< if test="id!=null"> id=#{id} < /if>
< /where>
< /update>
同理,trim标签也可以实现set标签的功能
foreach 标签:foreach标签实现批量删除

注:foreach标签可迭代任何对象(如列表、集合等)和任何的字典或者数组对象传递给foreach作为集合参数,当使用可迭代对象或者数组时,index是当前迭代的次数,item的值是本次迭代获取的元素。当使用字典(或者Map.Entry对象的集合)时,index是键,item是值。collection标签可以填(’list’,’array’,’map’)。
foreach元素的属性主要有 item,index,collection,open,separator,close。
item表示集合中每一个元素进行迭代时的别名;
index指 定一个名字,用于表示在迭代过程中,每次迭代到的位置;
open表示该语句以什么开始,
separator表示在每次进行迭代之间以什么符号作为分隔符;
close表示以什么结束。
